A clear introduction to definition and difference between DRAM and NAND Flash (end)
The action of writing to memory depends on capacitor charging or discharging by external data cable, resulting in completing the writing of 1 or 0 of digital data.
DRAM uses a MOS and a capacitor to store a bit of data (0 or 1). As shown in Figure 4 (a), when a MOS is not turned on, no electrons flow through it, and the capacitor has no charge. The data representing this bit is 0. As shown in Figure 4 (b), when a MOS is turned on (positive voltage is applied to the gate), electrons flow from the source to the gate. At this time, the capacitor is charged, and the data representing this bit is 1. In order to store these charges, a tiny capacitor must be used. As shown in Figure 4 (c), DRAM is slower than SRAM because its capacitor needs time to charge.

Figure 4: Schematic diagram of the structure and working principle of dynamic random access memory (DRAM).
Due to the leakage of capacitors, the memory will disappear due to insufficient potential difference. Therefore, unless capacitors are charged periodically, it is impossible to ensure that the data can be preserved for a long time.
Because the circuit structure of each DRAM basic memory unit is very simple, DRAM has low power consumption and low price. In this way, DRAM chips with large storage capacity can be manufactured at low cost. However, its disadvantage is that slow speed of reading and writing (capacitor needs to charge and discharge continuously) affects the performance of DRAM.
On the contrary, the structure of SRAM is more complex, which consists of six MOSs. We can label them with M1, M2, M3, M4, M5 and M6, respectively. These six MOSs need to be combined together in order to store one bit of data.
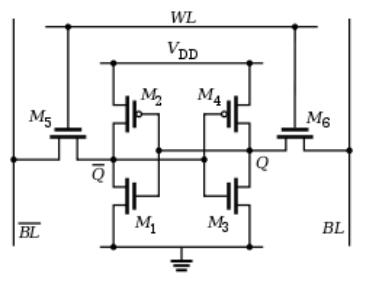
Different from DRAM chips, SRAM chips do not need to be separated into row addresses and column addresses. In addition, SRAM design is relatively more flexible. The number of memory units corresponding to an address can be 8 bits, 10 bits, or 32 bits, 40 bits, 64 bits.
Besides, the switching speed of MOS is much faster than that of capacitor charging and discharging, so the reading and writing speed of SRAM is much faster than that of DRAM.
However, if storing a bit of data in SRAM, six MOSs are required. As the number of MOSs increases, the size of chip becomes larger, which leads to the problem that integrated circuits become more larger and more expensive.
The price of SRAM is more than 1000 times higher than that of DRMA. For example, the price of SRAM per unit is $60/MB, while that of DRAM is $0.06/MB.
At the same time, each MOS consumes electricity. The more MOSs there are, the higher power consumption. Considering the high price and high power consumption, SRAM can only be used in some very harsh situations, such as cache memory mentioned above.
As a result, at present, DRAM is still used as main memory, while SRAM is used as cache memory with fast speed. However, both DRAM and SRAM belong to volatile memory, for the data stored will be lost without power supply.
Ferroelectric Random Access Memory (FRAM)
Dynamic random access memory (DRAM) is based on a MOS plus a capacitor to store a bit of data. The capacitors of traditional DRAM use silicon oxide as insulator. However, the dielectric constant of silicon oxide is not large enough (K value is not large enough), so it is not easy to attract (store) electrons and electric holes, resulting in the need to constantly replenish electrons and electric holes. That is the reason why it is called "dynamic". As long as the power of computer is turned off, the electrons and electric holes stored in the capacitor will be lost, and then, the data stored in DRAM will also be lost.
To solve this problem, the simplest way is to use materials with large dielectric constant (K value is large enough) to replace silica oxide as insulator, so that electrons and electric holes can be stored in capacitors without loss. At present, the industry usually uses ferroelectric material such as piezoelectric ceramic transducer (PZT) or strontium bismuthate tantalum (SBT) with large dielectric constant (K value) to replace silicon oxide. Ferroelectric material can store electrons and electric holes without loss, contributing to the original volatile dynamic random access memory (DRAM) becoming non-volatile memory. The non-volatile memory is famous as Ferroelectric RAM (FRAM).
What is NAND Flash?
Let us continue to talk about the non-volatile part.
Flash has been used in hard disks of various electronic products due to its advantages of light weight, small size and low consumption. Flash can be divided into NOR Flash and NAND Flash.
NOR Flash was introduced into the market earlier than NAND Flash. Its reading speed is fast, while writing speed is slow. In addition, NOR Flash is more expensive than NAND Flash.
NOR Flash has been used to store operating system code or important data. Therefore, NOR Flash can be made into ROM. After MXIC, a NOR Flash plant in Taiwan, enters the ROM supply chain of Nintendo Switch mainframe, its revenue rise this year.
NAND Flash is the most popular because of its fast writing speed and low price. Nowadays, USB hard disk and mobile phone storage is using NAND Flash technology.
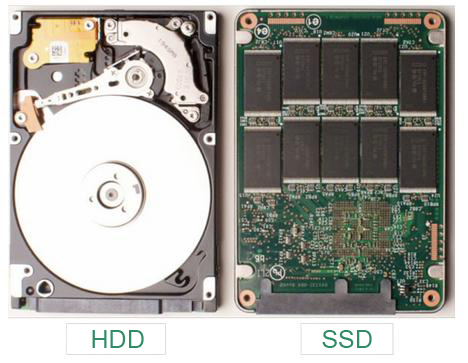
In addition, Solid State Drive (SSD) is also a storage device based on NAND Flash. SSD is not like the traditional hard disk (HDD) with motor, read-write arm and other parts. Slow speed, high power consumption, and considerable sensitivity to vibration make it difficult for HDD to be used in small operating devices.
On the contrary, SSD can read and write data without any noise. Thanks to fast speed, good resistance to vibration and light weight that less than one-tenth HDD, now SSD has become the mainstream storage device for personal computers and laptops.
Conclusion:
According to whether data can be retained if power supply is stopped, memory can be divided into volatile and non-volatile memory.
Volatile memory is divided into DRAM and SRAM.
SRAM is faster but more expensive, so main memory uses DRAM more, while cache memory often uses SRAM.
Non-volatile memory is divided into ROM and Flash. It is mainly used as hard disk.
