Don't be silly. Popular science: What's the difference between memory and storage?(3)
3. Difference among SLC, MLC and TLC NAND
Devices based on NAND storage technology, whether U disk or SSD, or even SD card, will involve a problem of cost. Thus the product design is transformed from SLC to MLC, then to TLC. And even QLC will be come out in the future. What impact will SLC, MLC and TLC have on the users?
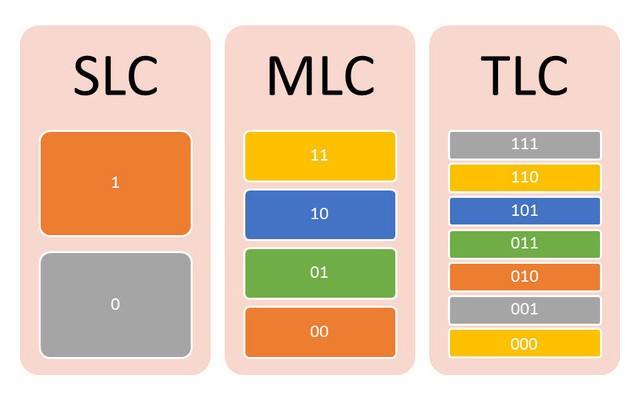
SLC--SLC (Single Level Cell——SLC)
SLC technology is characterized by a thinner oxide film in the floating gate and the source. When writing data, the stored charge can be eliminated by adding voltage to the floating gate and then passing through the source. In this way, one information unite can be stored. This technology can provide fast programming and reading, but is limited by the silicon efficiency. In order to upgrade SLC process technology, more advanced process enhancements must be adopted.
MLC--MLC (Multi Level Cell——MLC)
MLC was first developed by Intel in September 1997, whose function is to store two information units into a floating gate (the part of flash storage unit that stores charge), and then use different level charge to control accurate reading and writing through the voltage stored in memory. By using a large number of voltage levels, MLC stores two data in each cell, so that its data density is relatively high. SLC architecture has two values of 0 and 1, while MLC can store more than 4 values at a time, thus MLC architecture have a better storage density.
TLC--TLC (Trinary-Level Cell)
TLC is namely 3bit per cell. Each unit can store 1/2 more data than MLC, with a total of eight charging values. Thanks to requiring longer access times, it is slower in transmission speed. TLC has the advantage of low price when the production cost per megabyte is the lowest. However, it has a short life with only about 1000 erasures.
As mentioned above, the cell has a higher precision control of voltage from SLC to MLC and then to TLC, which directly causes the life of TLC to drop to only 1000 PE. As the corresponding SLC and MLC are 10000 and 3000, respectively, the durability of TLC decreases significantly.
Another disadvantage of TLC is the efficiency of reading and writing data. In SLC era, 1 cell only needs to read or write 1 bit at a time, while requiring 2 bit in MLC. What’s more, it rises to 3 bit in the TLC era. It is clear that its performance will become bad with the complexity of the program control by voltage. Of course, due to the continuous upgrading of technology and master control, TLC has catch up with MLC at present.
However, the durable injury of TLC cannot be effectively solved in a short time. Of course, its durability can be balanced wear by increasing capacity of storage devices, which prolong the service life of products in disguise.
Related Articles:
Don't be silly. Popular science: What's the difference between memory and storage?(1)
Don't be silly. Popular science: What's the difference between memory and storage?(2)
Explain the principle and use of NAND Flash with examples (2)
