How will SSD develop in data center in the future?
Various new technologies in the field of enterprise-class SSD emerges increasingly this year., including new storage media such as 3D XPoint and QLC SSD, as well as new products such as Open Channel SSD and customized SSD. Therefore, how will SSD develop in the future, and what types of mainstream media and products will it be?
During China Storage Summit just concluded this month, the author was fortunate to attend a presentation of Zhang Taile, vice president of products of Memblaze that is a Chinese enterprise-class SSD leader. As a veteran in SSD industry, Zhang analyzed the future of SSD in data center from both market and technology.
Will QLC SSD be popular in the enterprise-class market?
Every storage unit of QLC SSD stores 4 bits of data, while that of TLC SSD only stores 3 bits. Therefore, compared with TLC SSD, the cost of QLC SSD can be reduced by 25% even with the same technology. Therefore, many data center customers hope that QLC SSD can be deployed rapidly in storage nodes. What are major differences between QLC SSD and TLC SSD?
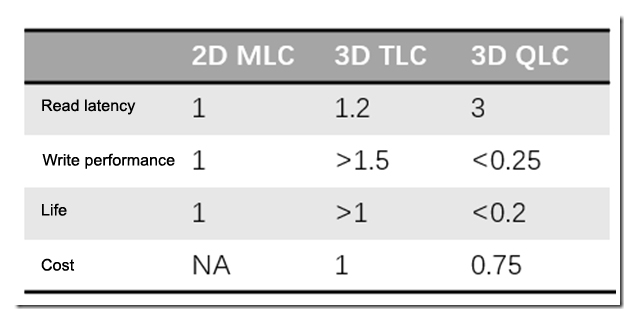
The following figure compares performance and cost among 2D MLC, 3D TLC and 3D QLC. The gap between QLC and TLC is much larger than that between TLC and MLC, mainly reflected in the following three aspects:
1. Read latency of QLC is 2.5 times that of TLC, leading to poor random read IOPS.
2. Write performance of QLC is one-sixth of TLC, reducing write bandwidth.
3. Life of QLC is only one-fifth of TLC. Some applications should be written with more than five-year scenarios. However, QLC probably run out in one year.
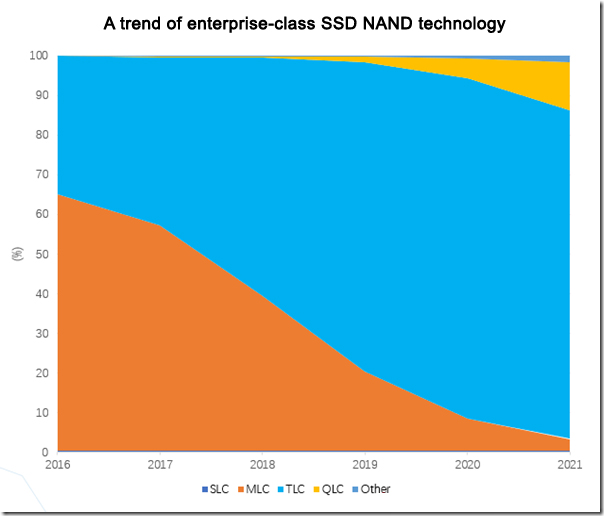
Value of 3D XPoint
QLC SSD is still far behind TLC SSD in performance, and can't become the mainstream of data center in the next five years. Is 3D XPoint SSD with better performance than TLC SSD hopeful to seize the SSD market?
As we all know, SSD gradually replaces traditional mechanical hard drive, and becomes the mainstream storage medium of data center, which depends not only on better performance than that of mechanical hard drive, but also on the decreasing cost which is expected to be lower than mechanical hard drive in the next five years.
Similarly, XPoint does not have as much performance advantage as SSD over HDD, and its cost is at least five times higher than TLC in the next five years. Therefore, XPoint is destined to become a minority choice only in the field of SSD in data center.
The real value of XPoint is to use it as NVDIMM in some scenarios requiring large memory. Considering long-term high memory price, XPoint is cheaper. XPoint can be used as memory to form a large data buffer in data center, where multiple CPUs or hosts can share data through high-speed Internet.
Will Open Channel SSD replace NVMe?
As Alibaba Data Center starts to customize Open Channel SSD, many SSD vendors are paying more and more attention to Open Channel SSD. Will Open Channel SSD replace NVMe SSD in data center in the future?
It seems difficult. The biggest problem is the lack of ecology and standards in Open Channel SSD. As shown below, PCIe SSD is based on private protocol in Fusion-IO era, which is not a problem at first. But when everyone starts to make PCIe SSD, users want to have a unified protocol as a standard. Thus, driven by big companies such as Intel and Samsung, NVMe has become a standard protocol.
Now, the ecology of NVMe SSD is becoming more and more mature. The most important thing of hardware products is standardization. Due to standards, SSD manufacturers can achieve the best reliability and stability through mass shipment and various optimization. More importantly, standardization can reduce costs and accelerate product import.
However, standardization also has its drawbacks, that is, it cannot meet the customization needs of customers. We should see that NVMe protocol is a rapidly updating protocol. At present, NVMe protocol has satisfied various customization requirements through IO-Determination, NVMe-KV and NVMe Over Fabrics and other new functions.
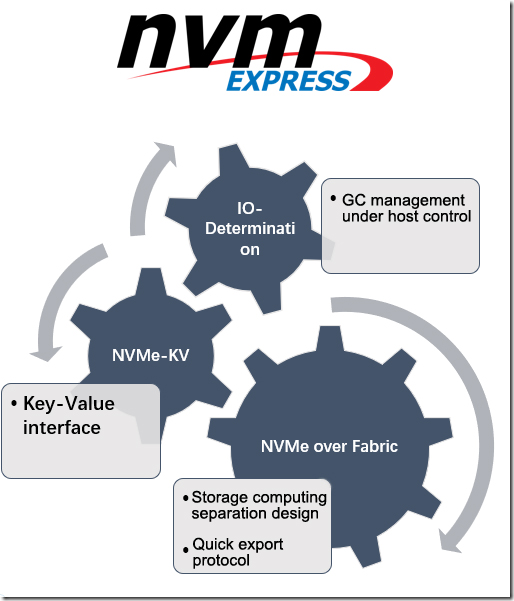
So NVMe SSD will be the mainstream of data center in the next five years.
What is the key to NVMe SSD in data center?
Of course, it’s core technology. Memblaze is a rare domestic company with mature and reliable ability to develop enterprise-level SSD firmware. It has taken nine years for continuous research and development in the field of enterprise-level SSD, and has successfully achieved nearly global PCIe SSD shipment of 100,000 pieces. It has to be said that Memblaze started its business quite hard and invested a lot of money, high-end talent and time.
With the rapid development of Chinese economy in recent years, many people are accustomed to making money rapidly and are unwilling to do core technology research and development that requires long-term technological investment. However, if Chinese enterprises want to compete with foreign companies in high-profit industries for a long time, core technology is indispensable.
Memblaze believes that the future of enterprise-class storage depends on PCIe SSD. If you want to be a leader in this industry, you must master core technology. Now, with the outbreak of enterprise PCIe SSD market, Memblaze's persistence for many years has finally paid off. The larger PCIe SSD shipments, the more stability and the less failure rate, because most of problems have been found and solved in the process of use. Now, R&D team of PCIe SSD with stable commercial and leading performance has become a scarce resource. When international giants want to enter enterprise-class PCIe SSD industry, they find they have fallen behind.
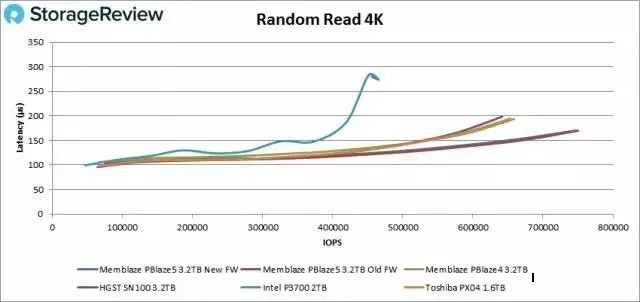
As shown below, Memblaze PCIe SSD Pblaze5 ranks first in random read IOPS and latency in the same batch tests in the evaluation from StorageReivew.
The following figure displays a low-power dual-port NVMe SSD developed by Memblaze. The left is a client server, and the right are two control hosts connected to the intermediate NVMe SSD. Typical working power consumption is only 10W, which can be used in dual-controlled full flash array. Storage power consumption is only 240W in a machine using 24 disks, when the capacity can be up to hundreds of TB.
There are three hotspots in enterprise storage technology in the future: SDS (Software Defined Storage), Hyper-Fusion and Full Flash Array. The storage media of these three products will be PCIe SSD. In the traditional storage field, the power of independent research and development in China is relatively weak. However, in the new storage era based on PCIe SSD, high-speed Ethernet and AI computing, Chinese storage companies have risen in an all-round way. We believe that several world-class enterprises will be born in the next ten years.
