Massive data and high-performance computing call for next-generation storage technology applications
Massive data and high-performance computing call for next-generation storage technology applications
Since 2016, the emergence of Internet of things and other technologies have driven the explosive growth of global Internet of things devices and generated mass data which has already become the key factor for deep learning, contributing to the development of AI . And, the processing of mass data also pushes up the demand for computing and storage, resulting in the emergence of high-performance computing. High-performance computing depends on the upgrading of memory technologies, giving rise to all kinds of next-generation memory technologies. Finding better memory solutions has become a priority for memory manufacturers.
What is next-generation memory? next-generation memory technologies refer to new memory technologies in the new era, including phase-change memory (PCM), ferroelectric memory (FeRAM), magnetoresistive RAM(MRAM), resistive RAM(RRAM or ReRAM) and many other new technologies.
High-performance computing has become the key item of scientific and technological development in the new generation.
In order to meet the increasingly heavy data processing requirements and workloads, the computing power continues to evolve, from functional computing beyond PC to workstations, to enterprise servers. Recently, with the introduction and popularization of intelligent networking devices, the introduction of network services has gradually evolved into a server group or data center. The workload of the network will continue to increase in the future, showing a trend of centralized computing, which is important and real-time but not private. Central (high-performance computing and cloud) processes confidential and non-real-time data, making high-performance computing important.
High-performance computing can finish complicated and extensive computing work in a limited or short time and improve the processing power of applications. Application fields include machine learning, deep learning, Internet of things and smart cities, etc.. The above application services reply on huge data for computing and training, most of which are consolidated by servers. In addition, with the development of virtualization platform and cloud storage technology, the requirements of servers have increasingly increased and driven the growth of Hyperscale Datacenter. According to topology survey, the number of global Hyperscale Datacenter is expected to reach 1,070 in 2025 and 13.7% of compound annual growth rate in 2016-2025.
A new solution to high-performance computing in the memory industry
With the help of high-performance computing, the Internet of things and smart applications, the next-generation memory has found a foothold and has gradually emerged.
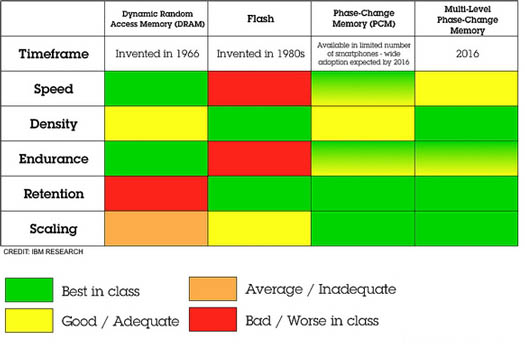
next-generation memory technologies include phase-change memory (PCM), ferroelectric memory (FeRAM), magnetoresistive RAM(MRAM), resistive RAM(RRAM or ReRAM) and many other new technologies. Nowadays, memory manufacturers, such as Intel, Samsung and Micron, have already input relevant development solutions. Take Intel's Optane as an example, it is a server product based on 3D XPoint design. Now it has introduced DIMM that is fully compatible with the server module in the market. For the host board design factory, the same slot can be freely changed to the server storage module or Optane solution based on the cost of the whole machine
3D XPoint is a non-volatile memory. Compared with NAND Flash, the read/write speed is 1,000 times different, and the service life is longer than NAND Flash. However, there is still a gap between 3D XPoint and NAND Flash application fields. NAND Flash has the advantage of high scale and low unit capacity, and it is difficult for 3D XPoint to compete with it in the short term. Compared with DRAM, 3D XPoint can meet certain conditions and has relatively low manufacturing cost, but it is still slower than DRAM. Therefore, currently, 3D XPoint cannot easily replace NAND Flash or DRAM.
Whether it can partially replace the market position of DRAM or NAND Flash, in the traditional memory market, there will still be gaps in the classical memory architecture that need to be filled to provide the stage for next-generation memory technology. In the case of the advantages and disadvantages of the next-generation memory and the existing solutions, the key to the volume is still the price consideration, and the most important factor to determine the current market price of the memory is the increase and decrease of the industrial inventory affected by demand and supply.
Both DRAM and NAND are now oversupplied, keeping prices for existing memory solutions down. In the case of DRAM, the continuous price decline is basically caused by the decline in demand for servers and smart phones, resulting in the consumption freeze and inventory rise. In addition to weak demand, NAND is prone to fall into the state of market competition due to numerous competitors. Moreover, the shift from 2D NAND to 3D NAND of different degrees leads to a substantial increase in supply bits. To sum up, DRAM and NAND prices will fall rapidly in 2019, and NAND prices are gradually approaching manufacturers' cash costs.
As the price of existing memory solutions has fallen sharply in 2019, it is not the best development condition for next-generation memory. However, looking into the future, the inventory replenishment momentum driven by successive demand recovery and price elasticity is expected to rebound the price of memory in 2020, giving the next- generation solution a better chance of volume. In particular, the Hyperscale Datacenter has a relatively high degree of customized design, which can plan new configurations for different memories. Topology believes that in the future, as the manufacturing cost of next-generation memory further decreases, the market will gradually increase the consideration and application of next-generation memory in special fields in the next few years, becoming another new option for existing solutions.
