The most comprehensive interpretation of USB Type-C Standard
ABIResearch, a market analyst, believes that we have reached the critical point for the commercial use of USB Type-C; by 2021, global shipments of smartphones equipped with such USB connectors are estimated to reach 830 million.
"Faster, Higher, Stronger" is our familiar Olympic motto, and if we apply this motto to the electronics industry now, it should be "faster, smaller, easier to use" - this is the cry of the new standard for USB connectivity.
As you may have seen, the latest USB Type-C (USB-C) ports are widely used in the new generation of computing products currently on sale, and this trend is expected to be further strengthened in the future, because USB-C has the unique ability to transmit data, power and even audio through a single wired connection.
USB Type-C (USB-C) is the latest standard of USB interface, and its application in various fields is rapidly popularizing. This paper introduces the performance characteristics of USB-C connectors, as well as the concepts and characteristics of related power and data transmission specifications such as USB PD and USB 3.1 related to USB-C. Taking the USB-C interface products of CUI Company as an example, it introduces the selection of USB interface products, which will help developers to understand the standard of USB-C deeply and select high-quality USB-C interface or cable components correctly.
The connector has a width of only 9 mm and a height of only 3.5 mm, which is much smaller than previous generations of connectors. It allows equipment manufacturers to develop smaller devices. And it comes at a time when it perfectly meets the needs of emerging products, such as home automation and Internet of things devices, including smart sensors that can be perfectly matched with this smaller, more concise, up-to-date connector package.
Undeniable ease of use
Cables for USB-C applications can be inserted from either end to meet the power requirements of laptops and other devices, so that users do not need to carry multiple cables for different purposes.
This versatility stems from the more complex structure within the connector (Figure 1). First, it has more wires. Unlike USB Type-A and Type-B connectors, which require four or five wires, the USB-C includes 24 contacts, allows two-way insertion, and supports four power and grounding pairs, as well as two signal pairs. In addition, its rated durability has increased to 10,000 plugs, a significant increase compared with the previous version of 1,500 plugs.
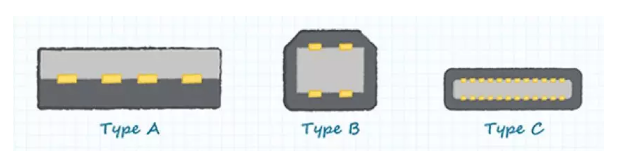
Figure 1:USB-C connector specifications are more stringent than earlier standards (picture source: CUI Inc.)
The rated voltage of the power supply and grounding pair of USB-C is up to 20V, and the current rating has also increased to 5A. It can provide up to 100W power transmission through a single USB-C connection. In addition, each pair of data pins can manage up to 10 Gbps of data transmission rate, which means that the connector has a total transmission capacity of 20Gbps.
The latest data and power specifications of USB-IF force us to greatly improve the transmission capability of USB-C, especially in the USB power delivery (USB PD), the high-speed data specifications of the second generation of USB 3.1 and the recently finalized USB 3.2:
USB PD makes full use of all four power supply and grounding pairs to give full play to the 100W power transmission capacity of USB-C.
The second generation of USB 3.1 defines the transfer rate of 10Gbps using a set of data channels.
Similarly, USB3.2 controls two groups of 10 Gbps data channels to maintain transmission rates of up to 20 Gbps.
Conceptually, it is important to distinguish the USB-C standard (which defines only physical connections) from USB PD and high-speed data specifications, including USB3.1 Generation 1 (SuperSpeed) and USB3.1 Generation 2 (SuperSpeed +), and USB 3.2.
For example, although the design of USB-C connector supports the standard of USB-PD, the host controller compatible with USB-PD is still necessary to negotiate and manage power transmission for interconnected devices. In addition, the cable must be configured to support the standard.
USB PDs not only increases the power, but also facilitates bidirectional power transmission, which can greatly improve the flexibility of charging and power supply for user equipment. On this basis, because USBPD can negotiate power through VBUS connection instead of using data connection, it can transmit power and data stream at the same time. And the table 1 shows the upgrading process of USB delivery capability in recent generations of products.
 specification.jpg)
Table 1: USB power delivery (USBPD) specification
In terms of high-speed data specifications, the second generation of USB 3.1 defines data and power signals, but does not specify physical connections, which enables us to use traditional Type-A or Type-B connectors and cables to connect USB 3.1 second-generation devices and achieve a data transfer rate of 10 Gbps, as long as they have sufficient current, voltage and signal integrity characteristics. Similarly, we can use USB-C connectors to provide traditional connection standards such as USB 2.0 by using simple hardware adapters.
Selection of high quality USB-C connectors
It is clear that not all USB-C connectors or cable assemblies are "born equal", and the high-quality products can provide better performance and show more reliable communication capability on longer cables.
In addition to considering the materials selected for future products and the quality of USB-C connectors, designers can also choose between two versions of Type-C sockets, as shown in Figure 2. Traditionally, standard SMT mounting sockets are located on top of PCB. But in this case, the total assembly height is the sum of PCB thickness and connector height. Alternatively, the intermediate mounting connector can be installed in the depression of the PCB; although this can reduces the total assembly height, the intermediate mounting connector does not allow the signal line to travel below the connector.
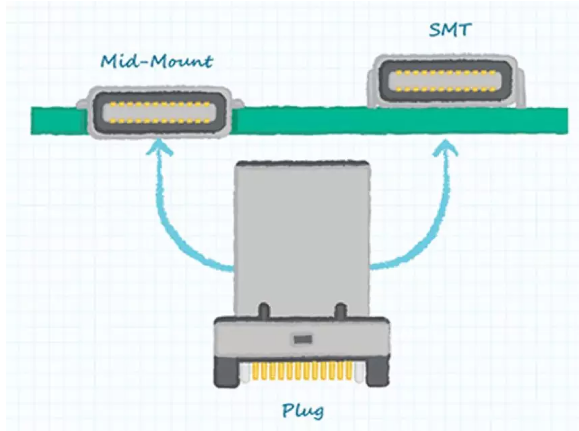
Figure 2:SMT and intermediate mounting USB-C connector (Picture Source: CUI Inc.)
Summary of this paper
In the market of consumer electronics, the application of USB Type-C connector is becoming more and more popular. To meet this growing demand, electronic component manufacturer CUI offers a range of high-quality USB Type-C plugs and sockets, including SMT and intermediate installation types. These connectors are designed to achieve the communication rate defined in the second generation specification of USB3.1, while meeting the current and future needs of designers.
